Details
A Guide to the Topic of Radiation Safety
Radiation is an integral part of medicine, nuclear power, and industry. Radiation has uses in the areas of altering medical diagnosis, electricity, and scientific research. Radiation is not without health risk, and staff, professionals, and the public need to be trained in radiation protection. Following is a summary of radiation protection, basic principles, protective procedures, and best practice for reducing risk.
What is Radiation?
Radiation is the release of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves or subatomic particles.
- It comes in two general categories:
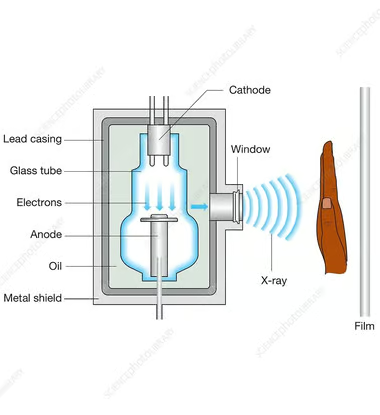
- Ionizing Radiation: Being powerful enough to remove electrons from atoms, ionizing radiation has the potential to damage tissue. X-rays, nuclear radiation and radioactivity, and gamma rays are only a few.
- Non-Ionizing Radiation: With less energy in the shape of radio waves, microwaves, and ultraviolet radiation, non-ionizing radiation is likely to be less damaging compared to ionizing radiation.
Sources of Exposure to Radiation
Radiation exposure most often occurs from
Natural Sources
- Cosmic Radiation: Comprising outer space and the sun.
- Ground Radiation: Released by radioactive material in water, rocks, and on land.
- Radon Gas: Radioactive gas that releases radiation from the ground and accumulates inside.
Artificial Sources
- Medical Imaging: X-rays, CT scans, and radiation therapy.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Plants that produce power in the form of electricity through nuclear reaction, which need to have adequately secured security systems.
- Industrial Uses: Used in material testing, food irradiation, and sterilization.
- Security Scanning: Airports and borders have security equipment that scans packages and freight using X-ray detectors.
- Radiation Protection Services: STAR NUKE offers radiation protection, safety instruction, and regulatory compliance services.
Principles of Radiation Safety
There are three basic principles utilized in order to lower the potential risk of radiation: Time, Distance, and Shielding.
1. Time: Dose received is decreased by shortening the period of exposure to radiation.
2. Distance: Radiation source is maintained at a distance to minimize exposure on the basis that intensity of radiation reduces with reduction in distance.
3. Shielding: Protective glass, lead aprons, or concrete walls absorb or minimize exposure to radiation.
Measurement and Dosimetry of Radiation
Radiation exposure both in units and technique is measured.
- Radiation dose: In Sieverts (Sv) or millisieverts (mSv) to quantify the effect on the body.
- Radiation exposure: In terms of Roentgens (R), or air ionization.
- Geiger Counter: Portable device to scan and measure the radiation intensity.
- Dosimeter: Badge issued to radiation-exposed areas workers to determine total dose.
Health Effects of Exposure to Radiation
The radiation effect is dose-, duration-, and type-dependent.
There are two in number:
Acute Effects (Short Duration and High Doses)
- Radiation burns
- Nausea and vomiting
- Damage to bone marrow
- Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
Chronic Effects (Long-Term Low-Dose Exposure)
- Cancer risk
- Genetic mutation
- Human organ damage
- Cataract development
Standards of Radiation Protection
Different international organizations offer the standards of regulation of exposure to radiation that comprise
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): They implement the safety standards for the application of radiation.
- World Health Organization (WHO): They study the health hazard of radiation and recommends them.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): It manages the United States workplace standard of radiation protection.
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP): Its mandate is to provide scientific advice towards facilitating radiation protection.
- Radiation Safety Organizations: Some organizations like STAR NUKE conduct hazard analysis, compliance audit, and radiation shielding with the guarantee of maintaining workplace safety.
Best Practices for Radiation Safety
To maintain a radiation-safe work environment while working with or in the presence of radiation, follow these practices.
1. Protective Equipment: Wear gloves, shields, and lead aprons when working with sources of radiation.
2. Industry and Regulatory Standards and Compliance Requirements
3. Monitoring of Radiation Dose: Ongoing monitoring of the radiation dose with dosimeters and other devices.
4. Installation of Engineering Controls: Minimization of radiation exposure by automation, ventilation, and shielding.
5. Training Employees and Informing: Routine emergency response and safety training.
6. Restrict Unnecessary Exposure: Use radiation only where it is necessary and standardize procedure to reduce dose to a minimum.
7. Safe handling of radioactives: Put the materials in their proper place with proper shielding and warning signs.
8. Report at once: Report and document at once any radiation leakage, overexposure, or spill.
Radiation Accidental Emergency Protocol
In case of an emergency of radiation, action must be initiated at once. The first things to do in this case are:
- Evacuation and Isolation: Evacuate the exposed workers from the source.
- Decontamination: Soap off and remove contacted clothes and wash the exposed contaminated body.
- Medical Examination: In the event of suspected radiation exposure, refer to a specialist medical doctor in an emergency.
- Warning: Inform responsible authorities and implement proper procedure containment.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Medical screening of the exposed patients to identify delayed effects.
Conclusion
Scientists, industrial workers, and health workers need information on protection from radiation. We can safely use radiation and avoid hazard through the use of protective practice, monitoring, and control. Being a health worker, industrial worker, or a merchant for radiation protection, utilizing the same makes an establishment better for protection. Organizations such as STAR NUKE come up with new concepts for protection from radiations to avoid being non-compliant and protect the workplace from radiations.

